DARIEN, IL – Facial features analyzed from 3D photographs could predict the likelihood of having obstructive sleep apnea, according to a study published in the April issue of the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine.
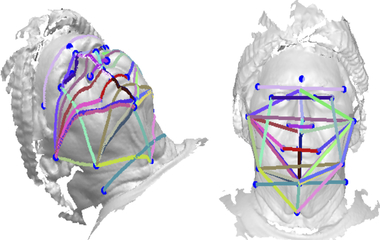
Using 3D photography, the study found that geodesic measurements — the shortest distance between two points on a curved surface — predicted with 89 percent accuracy which patients had sleep apnea. Using traditional 2D linear measurements alone, the algorithm’s accuracy was 86 percent.
“This application of the technique used predetermined landmarks on the face and neck,” said principle investigator Peter Eastwood, who holds a doctorate in respiratory and sleep physiology and is the director of the Centre for Sleep Science at the University of Western Australia (UWA). “Geodesic and linear distances between these landmarks were determined, and a linear discriminant algorithm was trained, tested and used to classify an individual as being at high or low risk of having obstructive sleep apnea.”
The study involved 300 individuals with varying severity levels of sleep apnea and 100 people without sleep apnea. These individuals came from a local hospital and from the Raine Study, a longitudinal cohort study in Western Australia. All underwent overnight sleep studies and took 3D photos with a craniofacial scanner system. Data were used to build a predictive algorithm that was tested on another patient set.
Eastwood worked with Syed Zulqarnain Gilani, a computer scientist at UWA to identify the facial features most commonly associated with sleep apnea as neck width and degree of retrusion of the lower jaw (retrognathia), but the study also uncovered other possible indicators.
“The data obtained from the present study indicate that other measurements such as width and length of the lower jaw, width of the face, and distance between the eyes also contribute to distinguishing individuals with and without OSA,” he said.
In a related commentary, also published in the April issue of JCSM, Drs. Ofer Jacobowitz and Stuart MacKay indicated that they see a bright future for 3D photography as a screening tool, potentially combined with data from a patient’s digital health tracker and health history.
“Certain wearable devices are already capable of measuring pulse oximetry and some provide oximetry variability analysis,” they wrote. “Likewise, the home of tomorrow will likely incorporate sensors in the bedroom which may gather physiological sleep data using optical, acoustic, infrared, ultrasonographic or other means.”
According to Eastwood, existing studies show a genetic predisposition to sleep apnea, and facial structure is a significant component of such predisposition, leading researchers to seek an accessible, affordable method of screening based on facial characteristics. Eastwood believes that 3D facial photography could represent the first, inexpensive, widely available screening tool for sleep apnea.
“OSA is a huge public health problem, and despite effective treatments being available, many with OSA are currently undiagnosed,” said Eastwood. “Therefore, simple, accurate screening tools are needed to predict those who have OSA.”
###
There were no conflicts of interest reported by the authors.
To request a copy of, “Predicting sleep apnea from 3-dimensional face photography” or the commentary, “The faces of sleep apnea in the age of machine learning,” or to arrange an interview with the study author or an AASM spokesperson, please contact the AASM at 630-737-9700 or media@aasm.org.
The monthly, peer-reviewed Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine is the official publication of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, a professional membership society that advances sleep care and enhances sleep health to improve lives. The AASM encourages patients to talk to their doctor about sleep problems and visit SleepEducation.org for more information about sleep, including a searchable directory of AASM-accredited sleep centers.
What is the Raine Study?
The Raine Study is one of the largest prospective cohorts of pregnancy, childhood, adolescence and now early adulthood to be carried out anywhere in the world. The Raine Study’s purpose is to improve human health and well-being, through the study of a cohort of Western Australians from before birth onwards. Between 1989 and 1991, a total of 2,900 pregnant women entered the study, and 2,868 live births were recruited into the cohort. These children born into the study, their parents, their grandparents, and now their own children are part of one of the world’s most successful multi-generational pregnancy cohort studies.
The Raine Study is a joint venture between The University of Western Australia, Curtin University of Technology, Telethon Kids Institute, Women and Infants Research Foundation, Edith Cowan University, Murdoch University and The University of Notre Dame Australia and receives additional funding support from the Raine Medical Research Foundation and National Health and Medical Research Council.